COMMENT OF THE DAY: CURRENT HOUSTON AIR SMELL RATINGS, MINUS THE COFFEE PERFUME  “It seems like it’s getting worse. 4 out of 7 mornings when it used to be maybe 2 out of 7. I wonder if it’s because the east downtown coffee plant has been shutdown, no longer masking the more harsher notes.” [Jeff, commenting on The Houston Hurricane Pollution-Sniffing NASA Flight That Never Took Off] Illustration: Lulu
“It seems like it’s getting worse. 4 out of 7 mornings when it used to be maybe 2 out of 7. I wonder if it’s because the east downtown coffee plant has been shutdown, no longer masking the more harsher notes.” [Jeff, commenting on The Houston Hurricane Pollution-Sniffing NASA Flight That Never Took Off] Illustration: Lulu
Air Quality
THE HOUSTON HURRICANE POLLUTION-SNIFFING NASA FLIGHT THAT NEVER TOOK OFF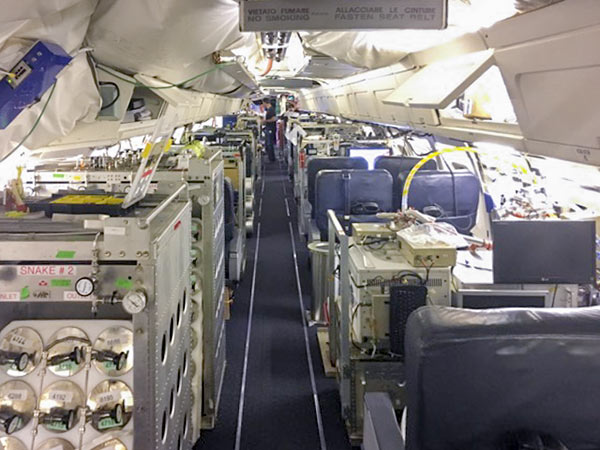  A week and a half after Hurricane Harvey hit Houston, as damage to smokestacks, pipelines, and chemical storage tanks were still being assessed, flooded Superfund sites went unmonitored, and clouds of benzene and other chemicals assembled in the skies over the city, the crew of a California-based airborne NASA chemical lab offered to help figure out the state of affairs — by diverting its specially equipped DC-8 from a planned trip to Oklahoma to take measurements in Houston instead. But EPA and TCEQ officials vehemently passed on the offer. An email response from TCEQ air toxicologist Michael Honeycutt noted that “state data showed no sign for concern,” report the L.A. Times‘s Susanne Rust and Louis Sahagun. “We don’t think your data would be useful for source identification while industry continues to restart their operations,” wrote Honeycutt, who the following month was appointed to head the EPA’s Science Advisory Board by President Trump. David Gray, the EPA official in charge of the Harvey emergency response, agreed. Citing emails from Texas officials “stating unambiguously that they do not want NASA to use the DC-8 for any data acquisition,” Michael Freilich, the director of NASA’s Earth Sciences division, called off the mission. [L.A. Times] Photo of Atmospheric Tomography Mission DC-8 interior, September 2017: NASA
A week and a half after Hurricane Harvey hit Houston, as damage to smokestacks, pipelines, and chemical storage tanks were still being assessed, flooded Superfund sites went unmonitored, and clouds of benzene and other chemicals assembled in the skies over the city, the crew of a California-based airborne NASA chemical lab offered to help figure out the state of affairs — by diverting its specially equipped DC-8 from a planned trip to Oklahoma to take measurements in Houston instead. But EPA and TCEQ officials vehemently passed on the offer. An email response from TCEQ air toxicologist Michael Honeycutt noted that “state data showed no sign for concern,” report the L.A. Times‘s Susanne Rust and Louis Sahagun. “We don’t think your data would be useful for source identification while industry continues to restart their operations,” wrote Honeycutt, who the following month was appointed to head the EPA’s Science Advisory Board by President Trump. David Gray, the EPA official in charge of the Harvey emergency response, agreed. Citing emails from Texas officials “stating unambiguously that they do not want NASA to use the DC-8 for any data acquisition,” Michael Freilich, the director of NASA’s Earth Sciences division, called off the mission. [L.A. Times] Photo of Atmospheric Tomography Mission DC-8 interior, September 2017: NASA
The U.S. Chemical Safety Board’s animated video (above) on the explosions at the Arkema Chemical Plant in Crosby recounts the steps taken by the brave workers stuck in charge of the facility in the aftermath of Hurricane Harvey. But a few angles less charitable to the company’s emergency planning effort aren’t included — possibly because they’d be a little more involved to animate. For example, the noxious fumes that emanated from the first fire, on the night of August 31, which according to a lawsuit filed later Arkema gave no warning about — and sent 23 people to the hospital, many of them vomiting and gasping for cleaner air.
And another detail: The remote detonations of 6 trailers containing unrefrigerated organic peroxides were carried out by the Houston Police Department’s bomb squad. “The entire police operation was conducted without warning the public,” write the Houston Chronicle‘s Matt Dempsey and Jacob Carpenter. “Until the documents were released earlier this month by the EPA, the public didn’t know who performed the controlled burn, or how it was done.”
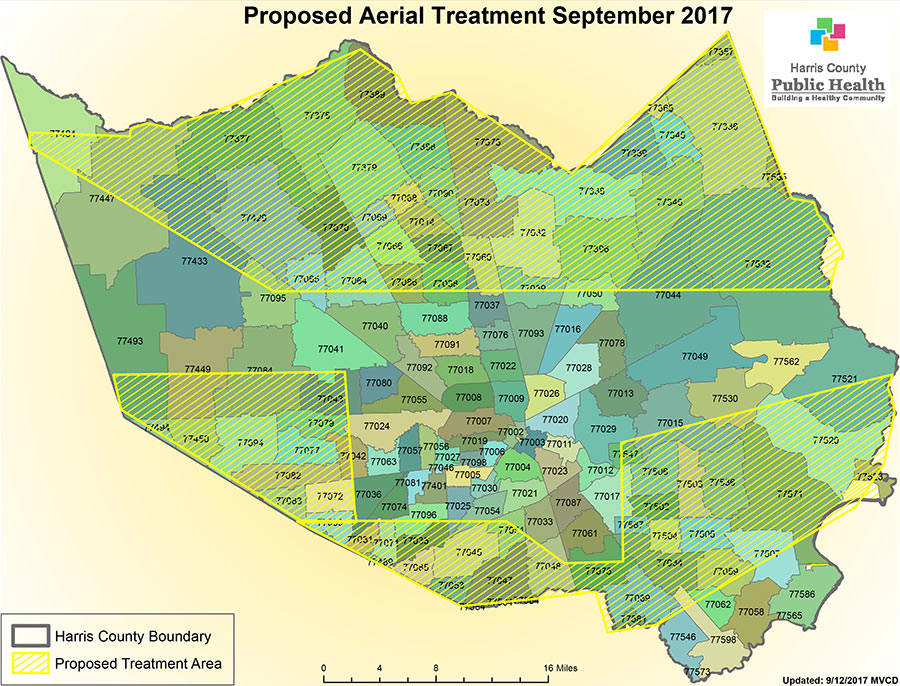
Here’s a map showing the 600,000 acres in Harris County over which the Air Force Reserve’s 910th Airlift Wing will be flying modified C-130 cargo planes staged from Kelly Air Force Base in San Antonio in order to conduct an aerial spray operation beginning Thursday evening. The marked zones to the north, south, east, and west of inside-the-Beltway Houston will be graced with a mist of Dibrom, an insecticide meant to reduce the threats posed by millions of mosquitoes arising from thousands of impromptu pools formed in Harvey’s wake. Harris County public health officials suggest persons “concerned about the exposure” — and area bees — remain indoors during the nighttime insecticide-disbursement procedure, which might take a second evening to complete.
- Aerial Mosquito Spray Operation Scheduled in Wake of Flooding [Harris County OHSEM]
Map: Harris County Public Health
SOMETHING POWERFUL IN THE CROSBY AIR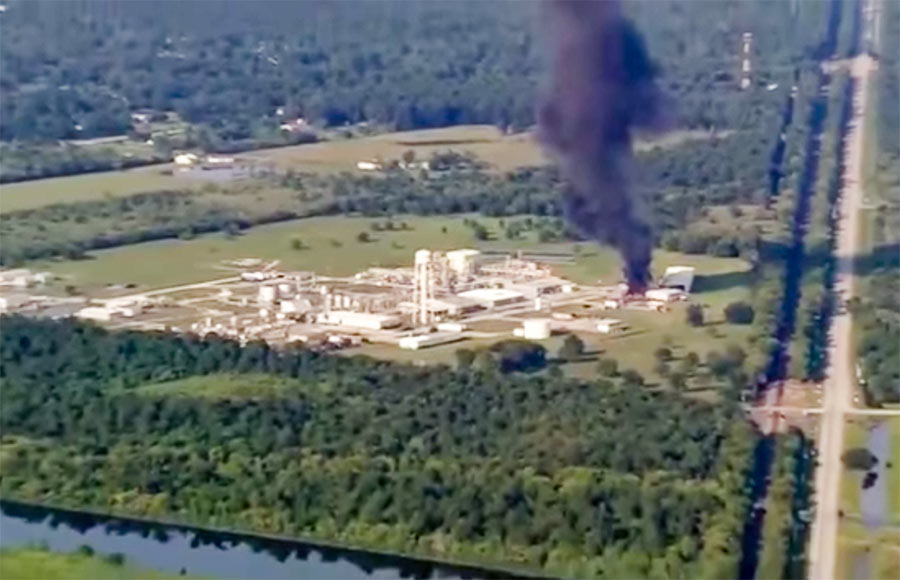  This vivid description is included in the original petition of a lawsuit filed today against Arkema, operators of the chemical plant off the Beaumont Hwy. in Crosby — by 7 first responders injured after incidents there last week: “In the early morning hours of August 31, 2017, the first of several explosions occurred as a result of the abandoned chemicals heating up and igniting. Although the explosions had occurred, no one from Arkema alerted the first responders who were manning the perimeter of the arbitrary mandatory evacuation area. Immediately upon being exposed to the fumes from the explosion. and one by one. the police officers and first responders began to fall ill in the middle of the road. Calls for medics were made, but still no one from Arkema warned of the toxic fumes in the air. Emergency medical personnel arrived on scene. and even before exiting their vehicle, they became overcome by the fumes as well. The scene was nothing less than chaos. Police officers were doubled over vomiting, unable to breathe. Medical personnel, in their attempts to provide assistance to the officers became overwhelmed and they too began to vomit and gasp for air. Some of the police officers. unable to abandon their vehicles due to their weapons being present, jumped in their vehicles and drove themselves to the nearest hospital. The other officers and medical personnel were all placed in an ambulance, and were driven to the hospital.†[Houston Chronicle; International Business Times] Still image of smoke from fire after Thursday’s explosion: abc13
This vivid description is included in the original petition of a lawsuit filed today against Arkema, operators of the chemical plant off the Beaumont Hwy. in Crosby — by 7 first responders injured after incidents there last week: “In the early morning hours of August 31, 2017, the first of several explosions occurred as a result of the abandoned chemicals heating up and igniting. Although the explosions had occurred, no one from Arkema alerted the first responders who were manning the perimeter of the arbitrary mandatory evacuation area. Immediately upon being exposed to the fumes from the explosion. and one by one. the police officers and first responders began to fall ill in the middle of the road. Calls for medics were made, but still no one from Arkema warned of the toxic fumes in the air. Emergency medical personnel arrived on scene. and even before exiting their vehicle, they became overcome by the fumes as well. The scene was nothing less than chaos. Police officers were doubled over vomiting, unable to breathe. Medical personnel, in their attempts to provide assistance to the officers became overwhelmed and they too began to vomit and gasp for air. Some of the police officers. unable to abandon their vehicles due to their weapons being present, jumped in their vehicles and drove themselves to the nearest hospital. The other officers and medical personnel were all placed in an ambulance, and were driven to the hospital.†[Houston Chronicle; International Business Times] Still image of smoke from fire after Thursday’s explosion: abc13
SMELLING BLIND IN THE EAST END  A possible cause of the nasty smells that caused East End residents headaches, sore and scratchy throats, and itchy eyes as Hurricane Harvey approached and inundated the area? Houston-area industrial plants in the last week released more than 2.25 million pounds of emissions above legal limits, according to an Environment Texas tally of Texas Commission on Environmental Quality data. The reason: plant shutdowns before the onset of the storm and startups after it left. “So far,” writes Emily Atkin, “TCEQ has not indicated these events have triggered health impacts. . . . TCEQ Media Relations Manager Andrea Miller told me the agency or local emergency officials would contact residents if an immediate health threat were to occur. What’s more, Miller said companies were probably reporting higher emissions that what actually occurred, ‘since underreporting can result in higher penalties.‘ It’s unclear, however, how TCEQ would check many of the companies’ reports, since the agency turned off all its air quality monitors in the Houston area before Harvey hit. Miller confirmed as much on Monday, saying devices were either turned off or removed “to protect against damage or loss of these sensitive and expensive instruments.†[The New Republic] Photo of ExxonMobil Baytown refinery: Louis Vest [license]
A possible cause of the nasty smells that caused East End residents headaches, sore and scratchy throats, and itchy eyes as Hurricane Harvey approached and inundated the area? Houston-area industrial plants in the last week released more than 2.25 million pounds of emissions above legal limits, according to an Environment Texas tally of Texas Commission on Environmental Quality data. The reason: plant shutdowns before the onset of the storm and startups after it left. “So far,” writes Emily Atkin, “TCEQ has not indicated these events have triggered health impacts. . . . TCEQ Media Relations Manager Andrea Miller told me the agency or local emergency officials would contact residents if an immediate health threat were to occur. What’s more, Miller said companies were probably reporting higher emissions that what actually occurred, ‘since underreporting can result in higher penalties.‘ It’s unclear, however, how TCEQ would check many of the companies’ reports, since the agency turned off all its air quality monitors in the Houston area before Harvey hit. Miller confirmed as much on Monday, saying devices were either turned off or removed “to protect against damage or loss of these sensitive and expensive instruments.†[The New Republic] Photo of ExxonMobil Baytown refinery: Louis Vest [license]
THE ASTRODOME’S FIRST SOLUTION TO ITS CAN’T-SEE-THE-BALL PROBLEM  Before players had that problem losing fly balls in the glare, before a portion of the skylights were painted over, before anyone in Houston had ever considered replacing the outfield grass with something called AstroTurf, there was another system installed in the Astrodome meant to help baseball players keep their eyes on the ball. The Houston Chronicle‘s special section on the Harris County Domed Stadium — on the occasion of its 50th anniversary (today) and birthday party open house (tonight) — includes a reprint (PDF) of the same newspaper’s Astrodome extra from April 8, 1965, the day before opening day. And featured on page 62 is a short preview of the stadium’s space-age air-cleaning technology: “An unusual Honeywell-engineered ultraviolet sensor will run a continual check on the transparency of the air. If it gets murky — from dust or tobacco smoke — the system will signal stadium engineers to open a battery of cupola exhaust dampers.
Because air cleaners continuously scrub the air electronically, then pass it through special charcoal filters to sieve out any odors, air inside the stadium normally will be fresher and cleaner than the air outside. ‘In fact, it should be the cleanest air in all Texas,‘ says Lamar Bordelon, Honeywell project engineer on the stadium job.
The Honeywell system has an ultraviolet lamp underneath the seats along the third-base line, focused on an ultraviolet sensor in similar position along the first-base line, 700 feet across the stadium. These continuously indicate the transparency of the air between them on a meter located on the control center. Any time the transparency of the air drops to the point where a player would have a hard time seeing a baseball in play 350 feet away, a warning light flashes on.” [Houston Chronicle] Photo: Russell Hancock
Before players had that problem losing fly balls in the glare, before a portion of the skylights were painted over, before anyone in Houston had ever considered replacing the outfield grass with something called AstroTurf, there was another system installed in the Astrodome meant to help baseball players keep their eyes on the ball. The Houston Chronicle‘s special section on the Harris County Domed Stadium — on the occasion of its 50th anniversary (today) and birthday party open house (tonight) — includes a reprint (PDF) of the same newspaper’s Astrodome extra from April 8, 1965, the day before opening day. And featured on page 62 is a short preview of the stadium’s space-age air-cleaning technology: “An unusual Honeywell-engineered ultraviolet sensor will run a continual check on the transparency of the air. If it gets murky — from dust or tobacco smoke — the system will signal stadium engineers to open a battery of cupola exhaust dampers.
Because air cleaners continuously scrub the air electronically, then pass it through special charcoal filters to sieve out any odors, air inside the stadium normally will be fresher and cleaner than the air outside. ‘In fact, it should be the cleanest air in all Texas,‘ says Lamar Bordelon, Honeywell project engineer on the stadium job.
The Honeywell system has an ultraviolet lamp underneath the seats along the third-base line, focused on an ultraviolet sensor in similar position along the first-base line, 700 feet across the stadium. These continuously indicate the transparency of the air between them on a meter located on the control center. Any time the transparency of the air drops to the point where a player would have a hard time seeing a baseball in play 350 feet away, a warning light flashes on.” [Houston Chronicle] Photo: Russell Hancock
COMMENT OF THE DAY: FOLLOW THE SMOG 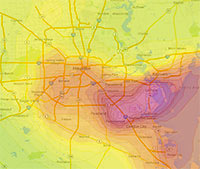 “You do not escape smog in Houston by moving to the burbs. In the summer, Houston has a circular wind pattern that takes ship channel pollutants for a ride out to the suburbs. Go to the Houston Clean Air Network website and set the animation for Aug. 6, 2012. You will see a big area of ozone form over the ship channel that gets blown out to Pearland, then Sugar Land and spends the late afternoon in Cinco Ranch and just east of Katy before starting to drift back east. The worst of the smog slides south of the City and never really gets north of I-10 inside the loop. Ship channel industries account for about 2/3rds of the smog. The rest is motor vehicle emissions. Ship channel industries have made significant progress in reducing and controlling emissions. But more sprawl and more traffic threaten to offset the progress made on the ship channel. Thus, the smog issue is a very real consequence of sprawl that is not escaped by sprawl either.” [Old School, commenting on Holding Back on That Downtown Hotel Push; The Beer Garden, Greenhouse, and Food Court Growing in Prohibition’s Basement] Image: Houston Clean Air Network
“You do not escape smog in Houston by moving to the burbs. In the summer, Houston has a circular wind pattern that takes ship channel pollutants for a ride out to the suburbs. Go to the Houston Clean Air Network website and set the animation for Aug. 6, 2012. You will see a big area of ozone form over the ship channel that gets blown out to Pearland, then Sugar Land and spends the late afternoon in Cinco Ranch and just east of Katy before starting to drift back east. The worst of the smog slides south of the City and never really gets north of I-10 inside the loop. Ship channel industries account for about 2/3rds of the smog. The rest is motor vehicle emissions. Ship channel industries have made significant progress in reducing and controlling emissions. But more sprawl and more traffic threaten to offset the progress made on the ship channel. Thus, the smog issue is a very real consequence of sprawl that is not escaped by sprawl either.” [Old School, commenting on Holding Back on That Downtown Hotel Push; The Beer Garden, Greenhouse, and Food Court Growing in Prohibition’s Basement] Image: Houston Clean Air Network
COMMENT OF THE DAY: WHY IS ANYONE LIVING THAT CLOSE TO A REFINERY?  “Tax policy should probably discourage residential habitation in neighborhoods near the Houston Ship Channel and encourage people to move away from them. As such, giving existing residents or residential property owners a tax cut in order to reward them for residing there or maintaining and leasing housing to other people would be extraordinarily counterproductive and stupid.
Manchester in particular is a neighborhood where the City or State government should seriously consider its options with respect to eminent domain. There’s nothing quite like it anywhere else in the region. Even the furthest north residential bits and pieces of Pasadena are better isolated from refinery activities and more integrated into their city than is Manchester.” [TheNiche, commenting on Baytown Buc-ee’s Is Here; Goodbye Mission Burrito, Hello Ãœberrito Mexican Grill] Illustration: Lulu
“Tax policy should probably discourage residential habitation in neighborhoods near the Houston Ship Channel and encourage people to move away from them. As such, giving existing residents or residential property owners a tax cut in order to reward them for residing there or maintaining and leasing housing to other people would be extraordinarily counterproductive and stupid.
Manchester in particular is a neighborhood where the City or State government should seriously consider its options with respect to eminent domain. There’s nothing quite like it anywhere else in the region. Even the furthest north residential bits and pieces of Pasadena are better isolated from refinery activities and more integrated into their city than is Manchester.” [TheNiche, commenting on Baytown Buc-ee’s Is Here; Goodbye Mission Burrito, Hello Ãœberrito Mexican Grill] Illustration: Lulu
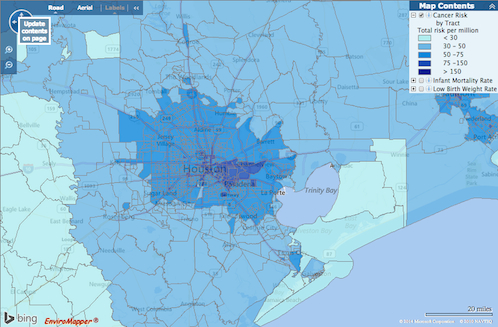
How do you feel about Houston’s airborne cancer hotspots? That’s easy! Just pick up a copy of the latest issue of Cite magazine and run your fingers over the top of it: Cite 93‘s front cover has been embossed with a map diagramming the area’s cancer risk. The places where airborne toxins mapped by the EPA are most prevalent are in the pits.
The mapped information here isn’t exactly fresh — it’s from the 2005 National-Scale Air Toxics Assessment, and the data only account for airborne known-cancer-causing toxins that are tracked by the EPA. Though it’s posted online, the map version isn’t exactly easy to find. But bravely thumbing his nose at Houston’s proud and longstanding tradition of hush-hushing location-based cancer hazards, Cite editor Raj Mankad gives Swamplot readers the secret recipe for finding the browsable map:
COMMENT OF THE DAY: HOW TO GET THAT SEWAGE SMELL OUT OF YOUR AIR CONDITIONING  “Had this same issue with our home in Midtown. The issue ended up being the air intake was not large enough where the filter was. Because of this, the blower would suck air from the drainage pipe in the pan for the hot water heater that was next to it. Removed the filter and reduced the stress of air coming through; the sewage smell went away.” [Mr.Clean19, commenting on Mysterious ‘Odor Beyond Our Control’ Forces Closure of Strip Center Chinese Restaurant in Spring] Illustration: Lulu
“Had this same issue with our home in Midtown. The issue ended up being the air intake was not large enough where the filter was. Because of this, the blower would suck air from the drainage pipe in the pan for the hot water heater that was next to it. Removed the filter and reduced the stress of air coming through; the sewage smell went away.” [Mr.Clean19, commenting on Mysterious ‘Odor Beyond Our Control’ Forces Closure of Strip Center Chinese Restaurant in Spring] Illustration: Lulu
COMMENT OF THE DAY: WHAT’S IN YOUR AIR  “There are three big air quality concerns for Houstonians: toxics, smog and particulates. Living in the East End puts you on the front line for toxic emissions. Toxics tend to be heavier than air and do not travel very far from where they are released. Milby Park had almost off the chart levels of Butadiene 1,3 back in mid 2000 due to problems at the Texas Petrochem plant next door. That problem was fixed and levels have come way down. But, if there is a release or a leak that is sending off toxics, the East End gets the best whiff. On days where there is little wind, the East End is also the spot most likely to get smog (NOx+SOx+sun=ozone). If there is good circulation in the atmosphere, Pearland to Sugar Land can see pretty bad smog, especially with the old coal plant in Sugar Land. But so can everywhere from Memorial Park up to the Woodlands. Houston’s smog has improved dramatically thanks to some good work by regulators and industry in identifying and going after the highly reactive stuff that really drives ozone production. But Houston is still in the top ten nationally when it comes to ozone. . . . Particulates are not as big a concern in Houston as we do not have much steel or other industries that are heavy on particulates, but we are still just over the new Federal standard of 12 parts per somethingerother. The particulates on the East End are generally higher than in other parts of town due to all the industry in the area. The air quality on the east side is definitely worse than on the west side. But ozone (smog) can visit just about anyone in the Houston area.” [Old School, commenting on Comment of the Day: The Limits of Eastward Development] Illustration: Lulu
“There are three big air quality concerns for Houstonians: toxics, smog and particulates. Living in the East End puts you on the front line for toxic emissions. Toxics tend to be heavier than air and do not travel very far from where they are released. Milby Park had almost off the chart levels of Butadiene 1,3 back in mid 2000 due to problems at the Texas Petrochem plant next door. That problem was fixed and levels have come way down. But, if there is a release or a leak that is sending off toxics, the East End gets the best whiff. On days where there is little wind, the East End is also the spot most likely to get smog (NOx+SOx+sun=ozone). If there is good circulation in the atmosphere, Pearland to Sugar Land can see pretty bad smog, especially with the old coal plant in Sugar Land. But so can everywhere from Memorial Park up to the Woodlands. Houston’s smog has improved dramatically thanks to some good work by regulators and industry in identifying and going after the highly reactive stuff that really drives ozone production. But Houston is still in the top ten nationally when it comes to ozone. . . . Particulates are not as big a concern in Houston as we do not have much steel or other industries that are heavy on particulates, but we are still just over the new Federal standard of 12 parts per somethingerother. The particulates on the East End are generally higher than in other parts of town due to all the industry in the area. The air quality on the east side is definitely worse than on the west side. But ozone (smog) can visit just about anyone in the Houston area.” [Old School, commenting on Comment of the Day: The Limits of Eastward Development] Illustration: Lulu
W. A. PARISH PLANT ONE OF THE WORST POLLUTERS IN THE COUNTRY, FINDS REPORT  According to a new study published by Environment America, NRG Energy’s coal-firing W. A. Parish Electric Generating Plant, on Smithers Lake outside of Richmond, is really good at being dirty. Though the plant has been messing around with a way to clean itself up in the past year or so, the report, published today, still fingers it as the 5th dirtiest in the country when it comes to carbon emissions. And here, in order, are 1-4: “Georgia Power Co.’s Plant Scherer, Alabama Power Co.’s James H. Miller Jr. Plant, Luminant’s Martin Lake in Texas, [and] Ameren’s Labadie in Missouri.” [StateImpact; Environment America; previously on Swamplot] Photo: Flickr user Joe A.
According to a new study published by Environment America, NRG Energy’s coal-firing W. A. Parish Electric Generating Plant, on Smithers Lake outside of Richmond, is really good at being dirty. Though the plant has been messing around with a way to clean itself up in the past year or so, the report, published today, still fingers it as the 5th dirtiest in the country when it comes to carbon emissions. And here, in order, are 1-4: “Georgia Power Co.’s Plant Scherer, Alabama Power Co.’s James H. Miller Jr. Plant, Luminant’s Martin Lake in Texas, [and] Ameren’s Labadie in Missouri.” [StateImpact; Environment America; previously on Swamplot] Photo: Flickr user Joe A.
STUDYING HOUSTON’S ROADSIDE AIR QUALITY  Another source of Houston’s pollution has got the attention of the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality: tailpipes. Starting in January, the agency will place a pair of monitors within 160 ft. of 2 our most heavily used roads — including the Southwest Fwy. near the Westpark Tollway — to record the amount of nitrogen dioxide leaked into the air. Apparently, the stuff can be pretty nasty, writes the Houston Chronicle’s Matthew Tresaugue: “The Environmental Protection Agency said studies have measured concentrations of the gas to be as much as 100 times greater near major roadways than away from them. Scientists, meanwhile, have linked the pollutant to asthma and other lung ailments, especially among children and the elderly.” The results of these monitors, adds Tresaugue, might lead the city to make decisions about preventing schools and residences from being built in and around affected areas. [Houston Chronicle ($); previously on Swamplot] Photo: AA Roads
Another source of Houston’s pollution has got the attention of the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality: tailpipes. Starting in January, the agency will place a pair of monitors within 160 ft. of 2 our most heavily used roads — including the Southwest Fwy. near the Westpark Tollway — to record the amount of nitrogen dioxide leaked into the air. Apparently, the stuff can be pretty nasty, writes the Houston Chronicle’s Matthew Tresaugue: “The Environmental Protection Agency said studies have measured concentrations of the gas to be as much as 100 times greater near major roadways than away from them. Scientists, meanwhile, have linked the pollutant to asthma and other lung ailments, especially among children and the elderly.” The results of these monitors, adds Tresaugue, might lead the city to make decisions about preventing schools and residences from being built in and around affected areas. [Houston Chronicle ($); previously on Swamplot] Photo: AA Roads
HOW HOUSTON’S AIR GOT BETTER  During the past decade, Houston’s notoriously polluted air has become — well, if not quite good, then not quite as bad, says NPR’s Richard Harris. (Pay no attention to what that ozone app may or may not tell you.) How? Well, it seems that pollution regulators in the early aughts had been worrying about all the wrong gases: “They were going all-in against [only] one of the pollutants that create smog, while downplaying the role of other emissions from the petrochemical plants,” reports Harris. “Barges carting chemicals up and down the [Ship Channel] were leaking. . . . And some types of storage tanks were leaking as well. . . . It turns out that routine day-to-day emissions were not the biggest problem.” Since then, regulations targeting those chemicals, like ethylene — as well as the use of infrared cameras that can spot them — appear to have made a difference: Port of Houston Authority employee Dana Blume tells Harris: “I can look out of my office window now and almost every single day see downtown.” [NPR; previously on Swamplot] Photo: Flickr user stmu_mike
During the past decade, Houston’s notoriously polluted air has become — well, if not quite good, then not quite as bad, says NPR’s Richard Harris. (Pay no attention to what that ozone app may or may not tell you.) How? Well, it seems that pollution regulators in the early aughts had been worrying about all the wrong gases: “They were going all-in against [only] one of the pollutants that create smog, while downplaying the role of other emissions from the petrochemical plants,” reports Harris. “Barges carting chemicals up and down the [Ship Channel] were leaking. . . . And some types of storage tanks were leaking as well. . . . It turns out that routine day-to-day emissions were not the biggest problem.” Since then, regulations targeting those chemicals, like ethylene — as well as the use of infrared cameras that can spot them — appear to have made a difference: Port of Houston Authority employee Dana Blume tells Harris: “I can look out of my office window now and almost every single day see downtown.” [NPR; previously on Swamplot] Photo: Flickr user stmu_mike

