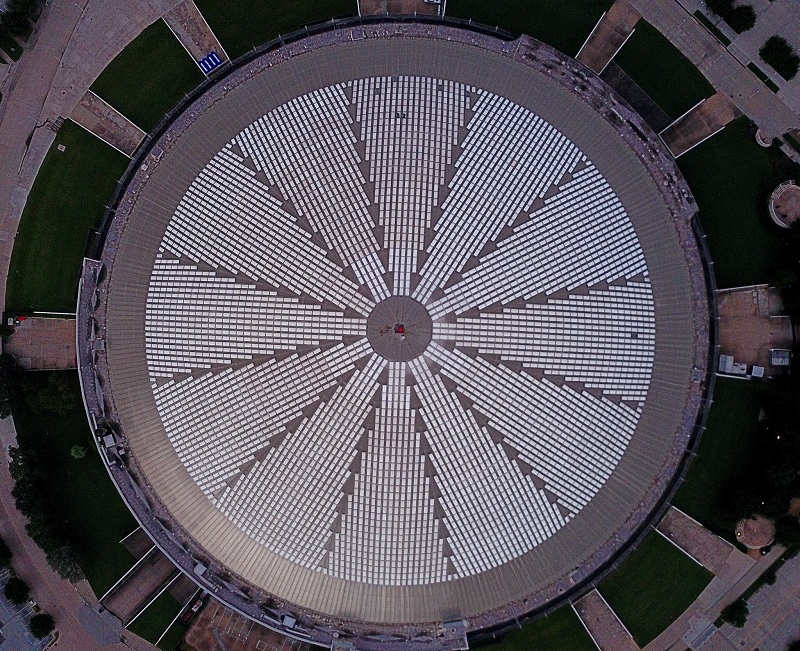
While hammering out the details of the Astrodome’s climate control system back before the building existed, members of the design team planned for some pretty bizarre weather not just outside it, but inside its 9.5-acre interior as well. According to I.A. Naman, whose firm designed the stadium’s air conditioning, “An experience had been reported previously regarding large dirigible hangars where unusual weather conditions were reported to have resulted in rainfall inside the hangar, even though it was not raining outside.” He wasn’t joking. “There was speculation that we might have such a situation in the stadium where fog, haze, self-generated turbulence in the nature of a tornado, cloud formations or even rain, might conceivably be experienced,” he wrote in 1966. “Was this something which really could happen or was it only a fear with no real basis?”
That the air inside the stadium would likely be filled with tobacco smoke made things even more complicated. If the smoke were to form a cloud of sufficient density, the engineers worried that it might obscure the audience’s view of what they came to see. “It was impractical to try to eliminate the smoke cloud entirely,” wrote Naman. So the question became: How much smoke could there be before the action on the field became too hard to follow? To find out, “A simple experiment was arranged,” he wrote. A few engineers sat down inside a sealed glass box. Outside the box, an attendant flicked on a color movie of a baseball game. Slowly and carefully, smoke was piped into the box until the engineers could no longer discern the game. A measurement was taken, indicating the maximum amount of haze a spectator could conceivably put up with. It became the target level that the design team strove to meet.
In order to reach it, they concluded:





 “Great to see that a bill
“Great to see that a bill 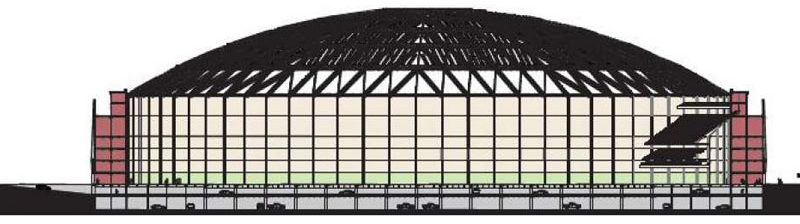

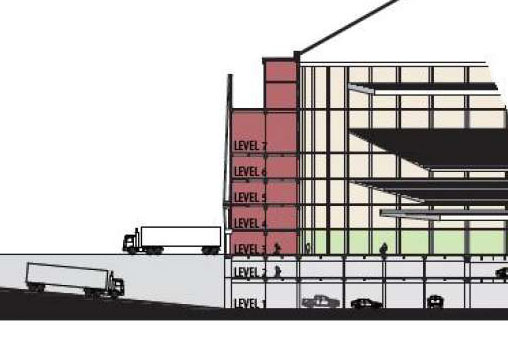 The Texas senate’s committee on intergovernmental relations gave an early stamp of approval toÂ
The Texas senate’s committee on intergovernmental relations gave an early stamp of approval to  “We’ve already got a built structure that has housed people in distress
“We’ve already got a built structure that has housed people in distress 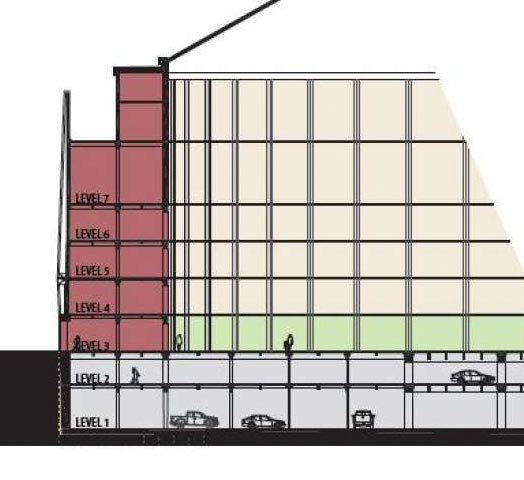 Here’s the statement judge Ed Emmett’s office just released
Here’s the statement judge Ed Emmett’s office just released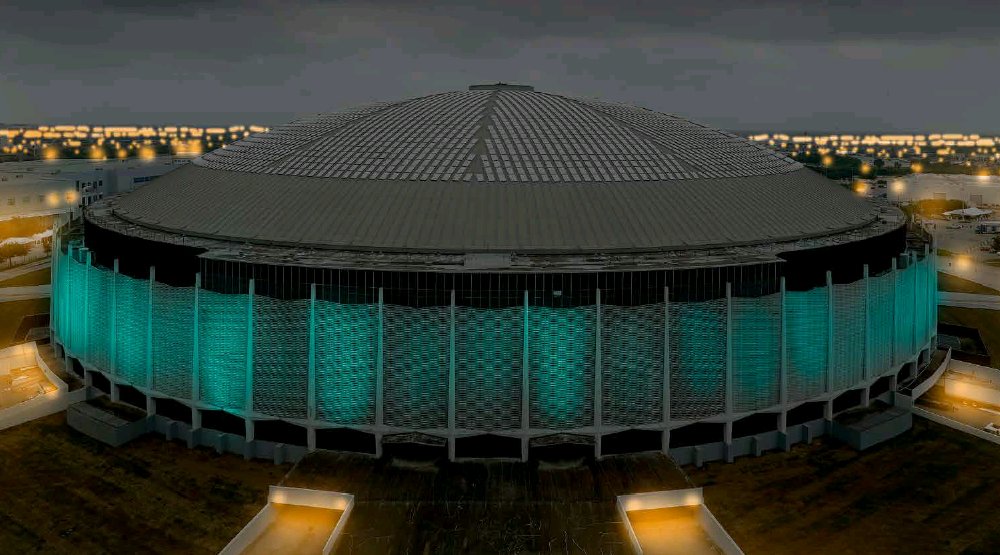 
 There’s a new tell-all biography of the Astrodome out this fall, now that year 50Â since the stadium’s mid-1965 opening has wrapped up.
There’s a new tell-all biography of the Astrodome out this fall, now that year 50 since the stadium’s mid-1965 opening has wrapped up.  The National Trust for Historic Preservation — that’d be the folks that
The National Trust for Historic Preservation — that’d be the folks that  “I think people are missing the larger view here. Of course there is plenty of current surface parking — but putting parking beneath the Dome begins to open up the possibility of densification on this site and on the old Astroworld site. This is the first, and necessary, step in transforming this entire area. I am betting that in 20 years or so this site will barely resemble the vast wasteland of parking lots and open space that it is today.” [
“I think people are missing the larger view here. Of course there is plenty of current surface parking — but putting parking beneath the Dome begins to open up the possibility of densification on this site and on the old Astroworld site. This is the first, and necessary, step in transforming this entire area. I am betting that in 20 years or so this site will barely resemble the vast wasteland of parking lots and open space that it is today.” [