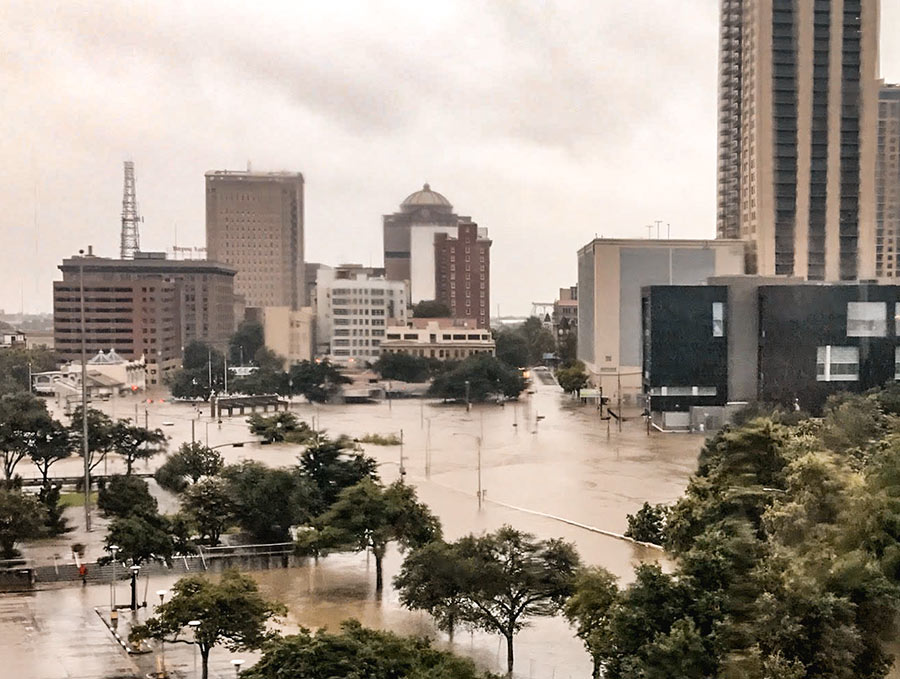
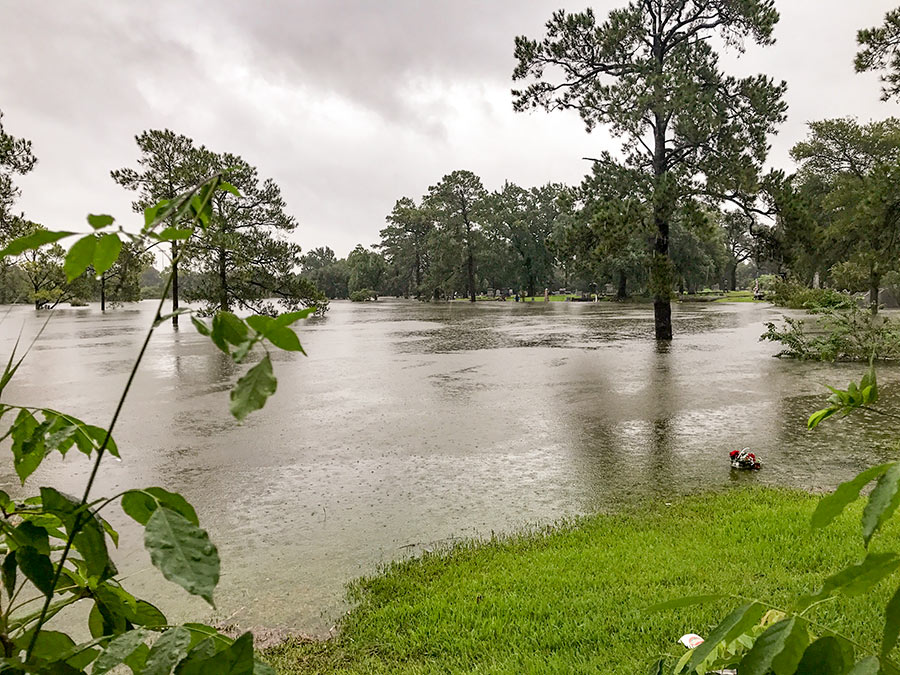
If you or someone you’re helping has been accepted into FEMA’s Transitional Shelter Assistance program — meant to clear out shelters by providing people who can’t return to their homes a hotel or motel room for a limited period of time — you may want to use the map shown here. It marks the locations of every eligible hotel or motel in the Houston area approved by the program. Using the map should make it easier to find an acceptable one nearby. To view the map in its own browser window, click here.
This map is yet another whipped-up-by-volunteers-in-a-jiffy product of Sketch City — this one created by the civic hacking group’s founder, Jeff Reichman. Sketch City volunteer and college sophomore Nile Dixon (who earlier created a similar tool to help people find nearby shelters) has created a simplified text-it-to-me version of it as well: Just text your ZIP Code to 832-981-4926 and a bot will send back contact info for the nearest verified accommodations in the program.
You can find out more about U.S. government Harvey assistance, including the TSA program, from the FEMA Harvey website.
- Map of FEMA-Approved Transitional Shelter Assistance Sites in the Houston Area [Sketch City]
- Texas Hurricane Harvey [FEMA]
- Sheltering And Immediate Assistance Available After Hurricane Harvey [DHS]
- Previously on Swamplot:Â How To Find Volunteers To Clear Out Your Flooded Home, and How To Volunteer To Help Clear Out Flooded Homes;Â The Best Way To Find Out Which Hurricane Harvey Shelters Near You Need Help, and What They Need;Â The Quickest Way To Find the Nearest Hurricane Harvey Shelter That Isn’t Already Full
Map: Sketch City
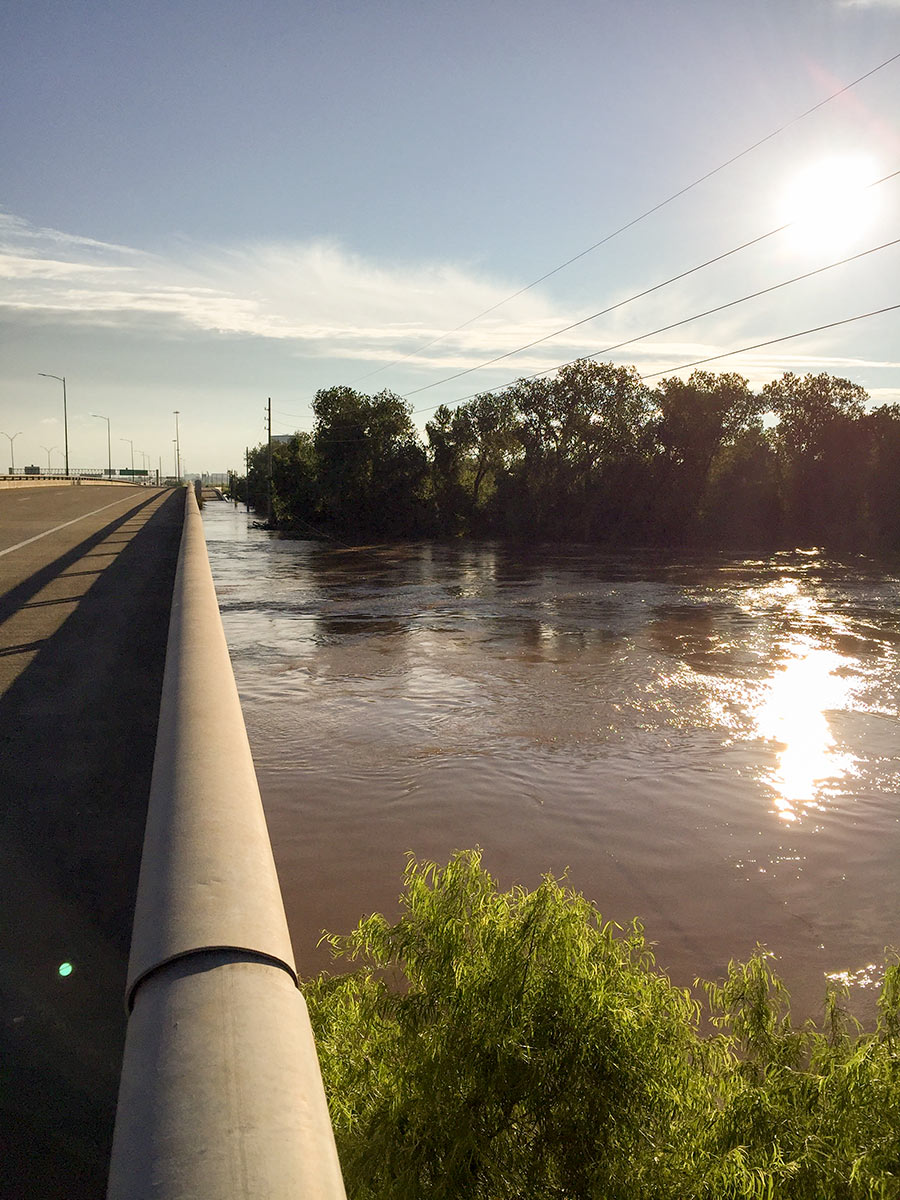

 It wasn’t until early this morning that the Brazos River in Sugar Land and Richmond
It wasn’t until early this morning that the Brazos River in Sugar Land and Richmond 


 “It is really amazing to look at the total disaster that Harvey caused (And Ike. And Allison. And the Tax Day flood. And the Memorial Day flood.) and say to developers and regulators in the Houston area, “Doing a heck of a job, Brownie.†Developers and regulators built thousands of homes and strip malls all across Houston during the boom cycles of the ’60s, ’70s, and early ’90s that had completely insufficient stormwater drainage infrastructure. Regulators allowed people to build too close to flood zones and builders did not think twice about building right up to bayous and rivers. The response from regulators was to require better development practices moving forward in some areas and apply a few band aids in other areas. This lax development attitude worked for a long time because it helped keep housing relatively affordable compared to other large metro areas. But after Harvey, people looking to come to Houston will have to consider whether the affordable housing and economic opportunities are worth the risk of losing everything in another big flooding event. The reassurance that developers are doing a better job with new projects does nothing to allay fears that existing housing is prone to devastating flooding. Houston’s failed development practices are now an albatross around the City’s neck.” [Old School, commenting onÂ
“It is really amazing to look at the total disaster that Harvey caused (And Ike. And Allison. And the Tax Day flood. And the Memorial Day flood.) and say to developers and regulators in the Houston area, “Doing a heck of a job, Brownie.†Developers and regulators built thousands of homes and strip malls all across Houston during the boom cycles of the ’60s, ’70s, and early ’90s that had completely insufficient stormwater drainage infrastructure. Regulators allowed people to build too close to flood zones and builders did not think twice about building right up to bayous and rivers. The response from regulators was to require better development practices moving forward in some areas and apply a few band aids in other areas. This lax development attitude worked for a long time because it helped keep housing relatively affordable compared to other large metro areas. But after Harvey, people looking to come to Houston will have to consider whether the affordable housing and economic opportunities are worth the risk of losing everything in another big flooding event. The reassurance that developers are doing a better job with new projects does nothing to allay fears that existing housing is prone to devastating flooding. Houston’s failed development practices are now an albatross around the City’s neck.” [Old School, commenting on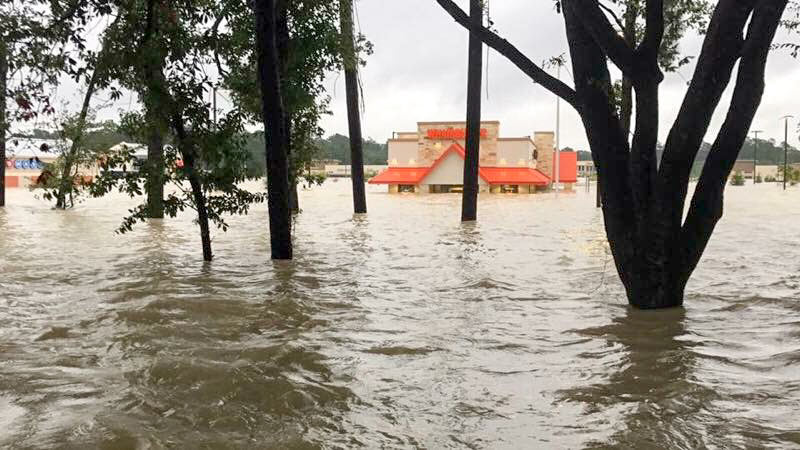 
 A possible cause of the nasty smells that caused East End residents headaches, sore and scratchy throats, and itchy eyes as Hurricane Harvey approached and inundated the area? Houston-area industrial plants in the last week released more than 2.25 million pounds of emissions above legal limits, according to an Environment Texas tally of Texas Commission on Environmental Quality data. The reason: plant shutdowns before the onset of the storm and startups after it left. “So far,” writes Emily Atkin, “TCEQ has not indicated these events have triggered health impacts. . . . TCEQ Media Relations Manager Andrea Miller told me the agency or local emergency officials would contact residents if an immediate health threat were to occur. What’s more, Miller said companies were probably reporting higher emissions that what actually occurred, ‘since underreporting can result in higher penalties.‘
A possible cause of the nasty smells that caused East End residents headaches, sore and scratchy throats, and itchy eyes as Hurricane Harvey approached and inundated the area? Houston-area industrial plants in the last week released more than 2.25 million pounds of emissions above legal limits, according to an Environment Texas tally of Texas Commission on Environmental Quality data. The reason: plant shutdowns before the onset of the storm and startups after it left. “So far,” writes Emily Atkin, “TCEQ has not indicated these events have triggered health impacts. . . . TCEQ Media Relations Manager Andrea Miller told me the agency or local emergency officials would contact residents if an immediate health threat were to occur. What’s more, Miller said companies were probably reporting higher emissions that what actually occurred, ‘since underreporting can result in higher penalties.‘ 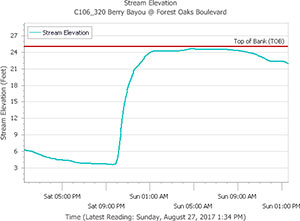 Chronicle features editor Lisa Gray says her Meadowcreek Village home escaped water damage during the flood, but it was close — and many others weren’t so lucky: “Berry Bayou — the middle of which forms my back property line,” she writes, “received more than 45 in. I’ve seen it in national weather-nerd articles where people are marveling how fast a bayou can rise. My husband says we were half an inch away from the bayou coming out of its bank in our back yard. He sent a graph, showing that on Saturday night, at the monitor I can see from my back yard, it was literally at bank level. But the water broke first on the other bank, into the yard of one of my favorite people in the neighborhood, and up and down the yards on that side. Lots of houses flooded. ‘Dry privilege’: That’s the headline of the essay I ought to write.” [
Chronicle features editor Lisa Gray says her Meadowcreek Village home escaped water damage during the flood, but it was close — and many others weren’t so lucky: “Berry Bayou — the middle of which forms my back property line,” she writes, “received more than 45 in. I’ve seen it in national weather-nerd articles where people are marveling how fast a bayou can rise. My husband says we were half an inch away from the bayou coming out of its bank in our back yard. He sent a graph, showing that on Saturday night, at the monitor I can see from my back yard, it was literally at bank level. But the water broke first on the other bank, into the yard of one of my favorite people in the neighborhood, and up and down the yards on that side. Lots of houses flooded. ‘Dry privilege’: That’s the headline of the essay I ought to write.” [
