CHARLES BARKLEY’S OLD HOUSE IS ABOUT TO HIT THE MARKET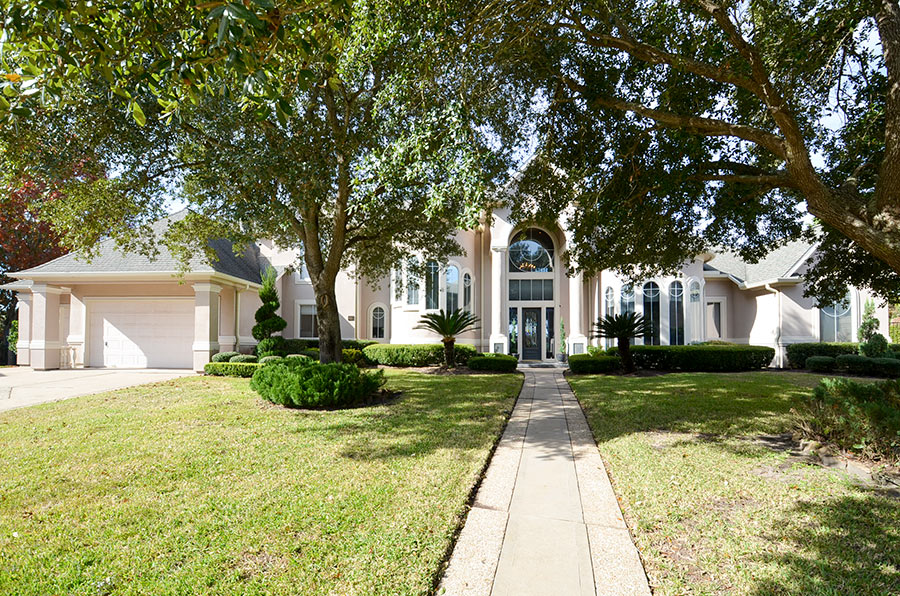  Two years after finishing his career with the Rockets in 2000, the power-forward-turned-broadcaster sold his Sugar Land house at 66 Harbor View Dr. to the current homeowners, who — according to a preview put out by ResideTX Properties — are about to put it back on the market. It sits at the back of a cul-de-sac in the Pointe Royale subdivision east of where New Territory Blvd. crosses the Grand Pkwy. Inside, 3,956 sq.-ft. houses 4 beds and 3.5 baths. [ResideTX] Photo of 66 Harbor View Dr.: ResideTX
Two years after finishing his career with the Rockets in 2000, the power-forward-turned-broadcaster sold his Sugar Land house at 66 Harbor View Dr. to the current homeowners, who — according to a preview put out by ResideTX Properties — are about to put it back on the market. It sits at the back of a cul-de-sac in the Pointe Royale subdivision east of where New Territory Blvd. crosses the Grand Pkwy. Inside, 3,956 sq.-ft. houses 4 beds and 3.5 baths. [ResideTX] Photo of 66 Harbor View Dr.: ResideTX
Featured Posts
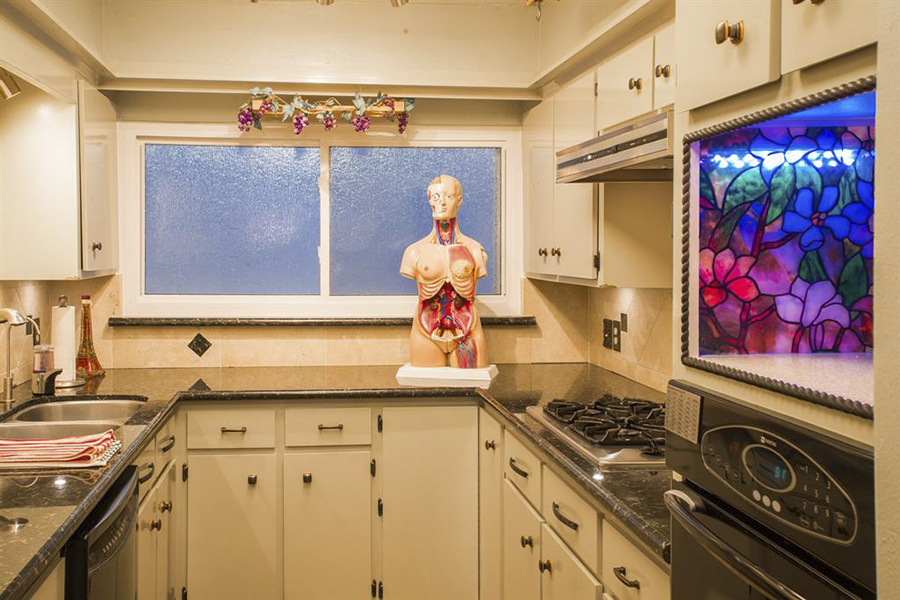


At least one resident of 224 Emerson St. doesn’t appear to be going anywhere. “The model” — dubbed Francis by the homeowners — “isn’t attached,” writes the listing agent, “but everything is negotiable.” His current kitchen counter hangout is tucked back on the ground floor of the condo — the furthest east of 6 on the block south of Hawthorne St. in Westmoreland — leaving the house’s more prominent spots available for other kinds of decor.
To get to the first one, head through the gate to the right of the garage door and step through the front door:
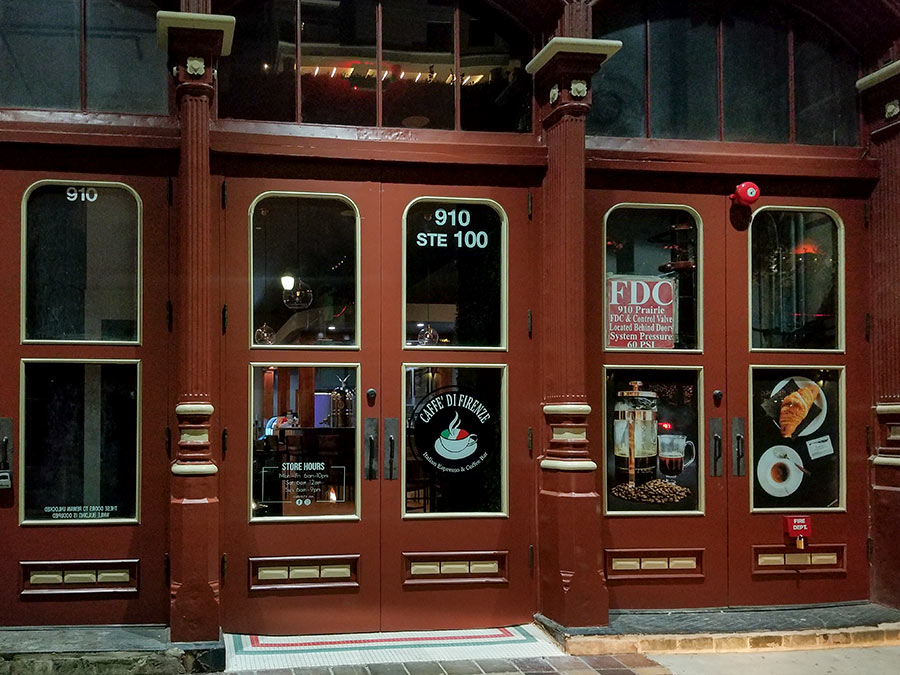


Note: We’ve appended a photo showing off Caffè Di Firenze’s espresso machine to the end of this story.
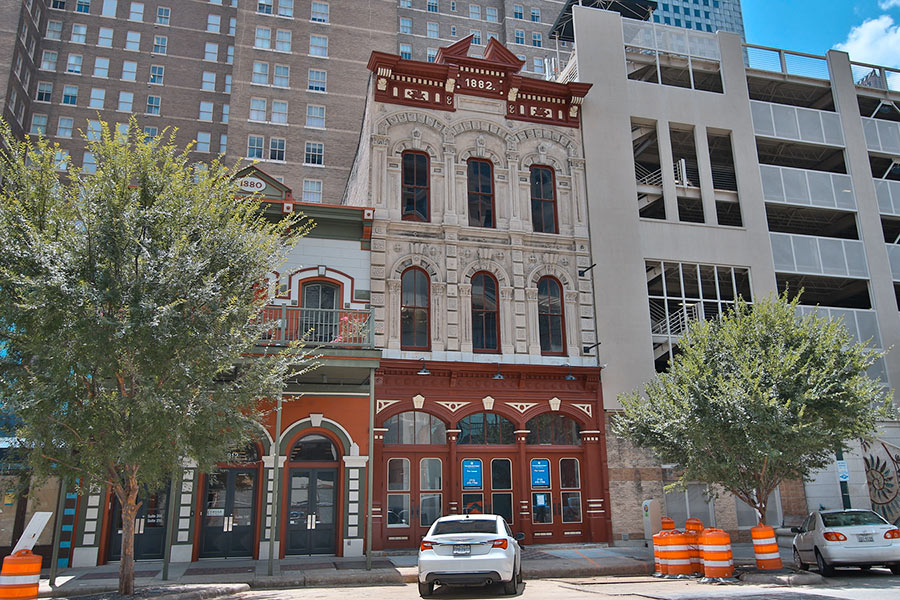
New signage is up in the windows of the Henry Brashear Building at 910 Prairie St. downtown on account of Caffè Di Firenze‘s recent move into the place. It’s now serving drinks and food inside and plans to do so on the outside, too, once the city signs off on permission for chairs and tables to go on the sidewalk. The photo at top shows the storefront pretty much the same as it’s been since going red in 2016. Except now some new tri-colored tiling peeks out from underneath the doors.
Inside, there’s this hashtagged wall of greenery:
ONCOMING TEXAS BULLET TRAIN MODEL NOW KILLING TIME IN JAPAN AHEAD OF ITS STATESIDE DEBUT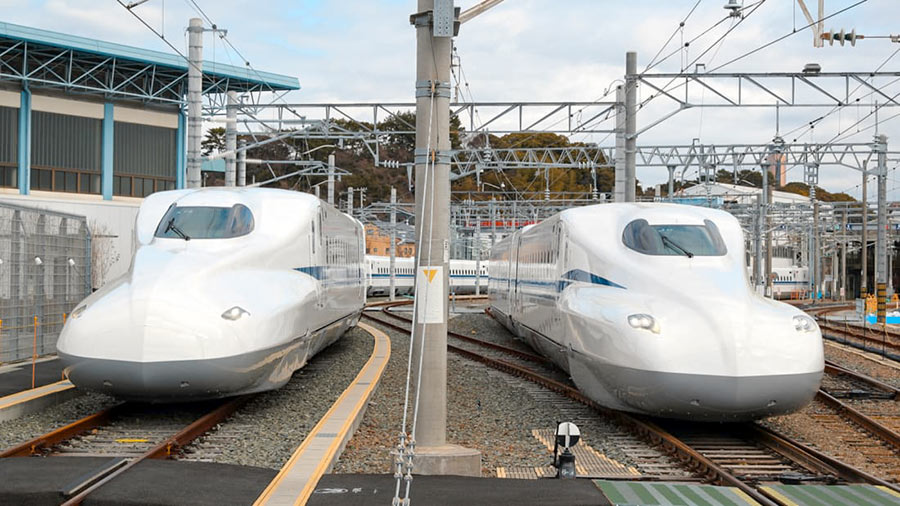  The general manager of Central Japan Railway Company, the Japanese firm designing the would-be Houston-Dallas bullet train, tells WFAA’s Jason Whitely it’ll be a spin-off of the company’s recently-revealed N700S model, 2 prototypes of which appear above. That new design — test runs of which began in July — is a half-size version of the N700 stock the company currently operates along Japanese rail lines: 8 cars instead of 16. They’re planned to start
The general manager of Central Japan Railway Company, the Japanese firm designing the would-be Houston-Dallas bullet train, tells WFAA’s Jason Whitely it’ll be a spin-off of the company’s recently-revealed N700S model, 2 prototypes of which appear above. That new design — test runs of which began in July — is a half-size version of the N700 stock the company currently operates along Japanese rail lines: 8 cars instead of 16. They’re planned to start hurdling hurtling down the country’s Shinkansen rail network at 177 miles-per-hour in 2020, by which time Texas Central — our state’s own high-speed rail hopeful — expects to have broken ground already on its 240-mile right-of-way. It says its version of the trains — to be named the N700I (“I” for “international”) will start off running at 186 miles-per-hour but could later accelerate up to 205, “subject to regulatory approval and market demands.” [WFAA; previously on Swamplot] Photo of 2 N700S Shinkansen prototype trains: Texas Central
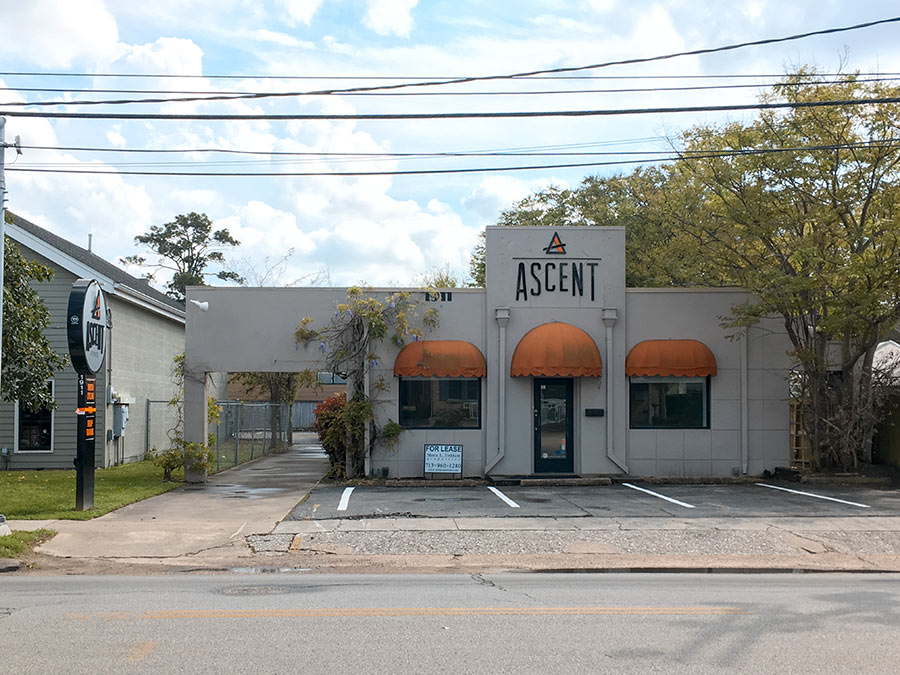


The former Ascent Fitness building next to West Alabama Ice House is taking on a new life as Blue Mambo Hair Salon, according to a building permit filed yesterday. The gym’s 3-year run in the 4,260-sq.-ft. space at 1911 W. Alabama ended last October following the on-site sale of all no-longer-needed exercise equipment. (It took over the building in 2015 from 713 Pilates, now located down the street in the strip center it shares with Siphon Coffee.)
“For lease” signs went up early this year around the property, which includes a back parking lot that wraps the next-door hardware store and kicks out onto Hazard St. That arrangement should give Blue Mambo a bit more space than it’s got currently in the Chelsea Market shopping center off Montrose Blvd., long rumored for some kind of highrise replacement.
Photos: Margo
ARMY CORPS’ FIRST PUBLIC IKE DIKE DISCUSSION IS TOMORROW 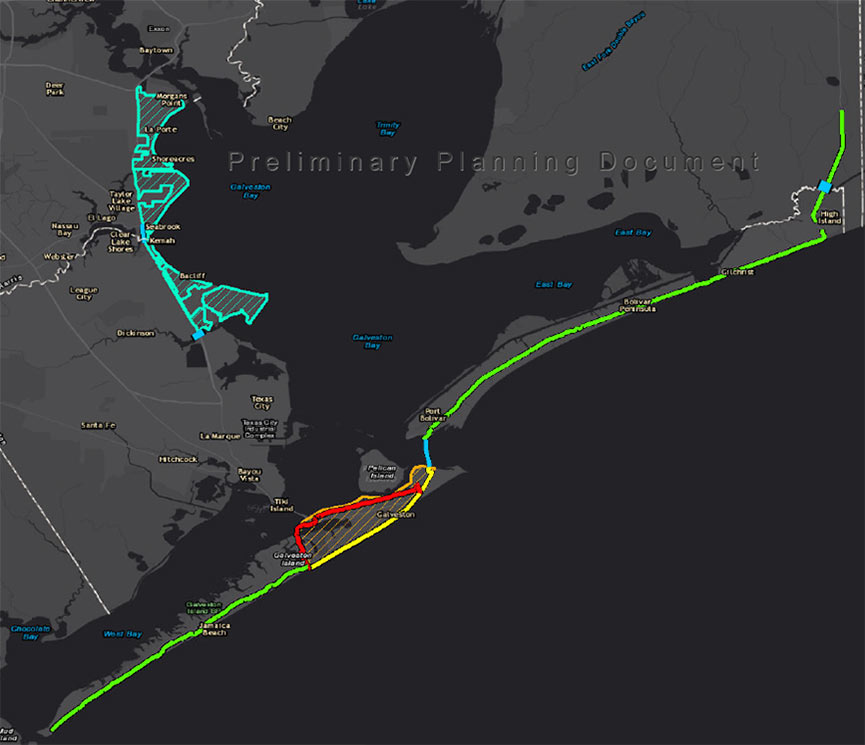 Tomorrow, the Army Corps will hold a public meeting in Port Lavaca about the Ike Dike it proposed last month. The meeting — the first of 6 planned between now and April — will give the agency an in-person opportunity to defend the modeling system underlying its $30 billion recommendations, which took some heat earlier this month from Rice U. scientists who claimed it didn’t take into account all those 100-year events that keep happening every few years. Since then, the Corps has told the Chronicle’s Nick Powell that isn’t true, adding that numerous key tweaks have brought the system up to date from FEMA’s earlier model, used in flood insurance mapping projects. The public comment period for the proposal remains open until mid-January. [Houston Chronicle ($); previously on Swamplot]
Tomorrow, the Army Corps will hold a public meeting in Port Lavaca about the Ike Dike it proposed last month. The meeting — the first of 6 planned between now and April — will give the agency an in-person opportunity to defend the modeling system underlying its $30 billion recommendations, which took some heat earlier this month from Rice U. scientists who claimed it didn’t take into account all those 100-year events that keep happening every few years. Since then, the Corps has told the Chronicle’s Nick Powell that isn’t true, adding that numerous key tweaks have brought the system up to date from FEMA’s earlier model, used in flood insurance mapping projects. The public comment period for the proposal remains open until mid-January. [Houston Chronicle ($); previously on Swamplot]
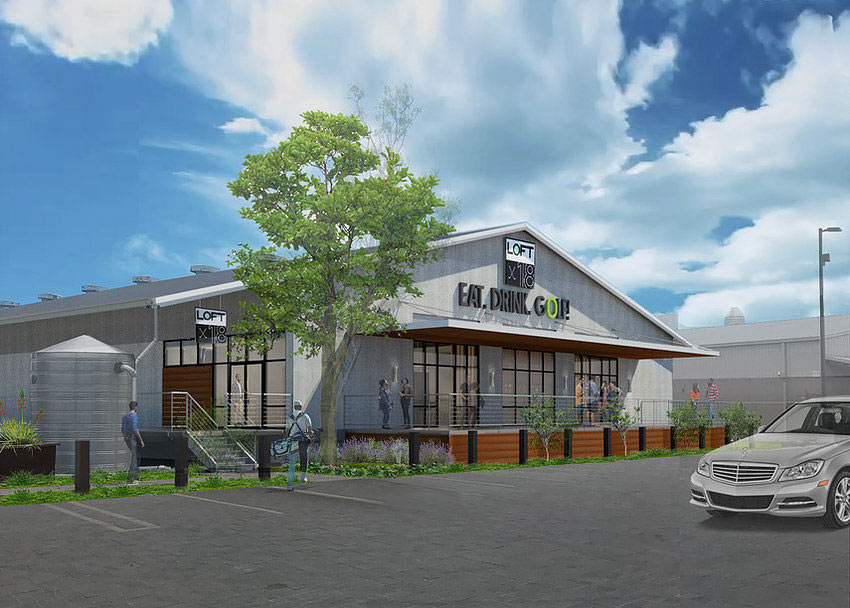

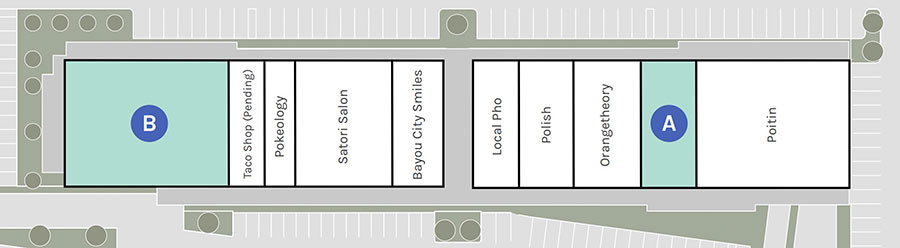
A new indoor golf venue is on its way into the Shops at Sawyer Yards, where it’s laid claim to the empty space marked “B” in the site plan above, adjacent to Sawyer St. It’ll be Loft18‘s first step outside Metairie, Louisiana, home to its only existing location. There, an array of 5 golf simulators — essentially turf teeboxes fronted by large video screens — offer customers 95 different courses to play. Along with bar and kitchen service, it’s all wrapped up within 7,000 sq.-ft.
The rendering at top shows what the west face of the converted warehouse building at 2313 Sawyer St. could look like once Loft18 gets situated. No building permits appear to have been filed yet on that address, however, HAIF users note that both a Houston-specific website and Facebook page for the business recently went live.
- Previously on Swamplot: Awesome Bites Will Take a Chunk Out of Shops at Sawyer Yards’ West Side; B&B Butchers Bull Marking New Territory in Shops at Sawyer Yards; Where Lovett Commercial Is Really Developing That Restaurant in the First Ward
Rendering: Loft 18. Site plan: Lovett Commercial
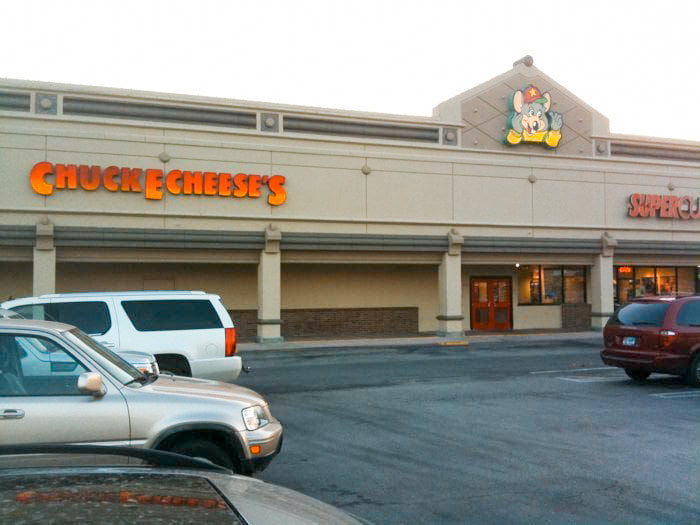

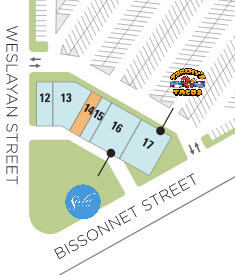
Work is underway to divvy-up the abandoned Chuck E. Cheese’s at the Weslayan Plaza shopping center into handful of new retailers. Among them: Torchy’s Tacos. It hasn’t fully materialized yet but looks good on paper in the updated site plan that Regency Centers is now showing off on its website. Next-door — and east of longtime tenant Skeeter’s Mesquite Grill — Sola Salon Studios (number 16) and Sally Beauty Supply (15) are also newcomers, themselves carve-outs from the former mouse-themed pizza and arcade joint as well.
It served its last slice earlier this year, by which time the house animatronic band — once a staple of all Chuck E. Cheese’ses — had presumably left the building. Company leadership axed the mechanical Pizza Time Players from all store locations last August, ending their 41-year nationwide run. “Back then,” Chuck E. Cheese’s top brass Tom Leverton told NPR’s Morning Edition, “kids’ expectations of technology were much, much lower.”
Photo: Phil L. Map: Regency Centers
ESCAPE ROOM CHAIN NOW GETTING SETTLED IN MID MAIN LOFTS 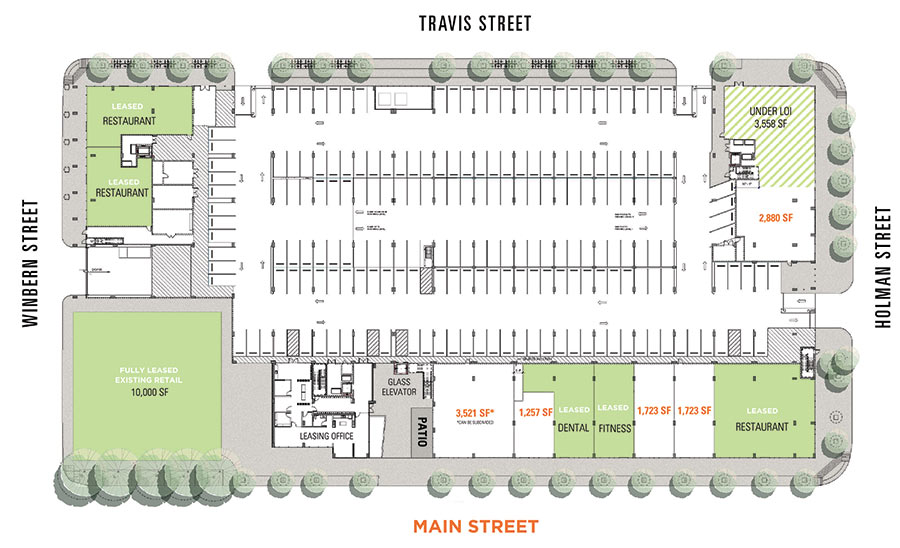 The latest tenant cropping up in the Mid Main Lofts’ Main-St. side: Project Panic, a 3,395-sq.-ft. escape room venue. Judging from the size and layout of the chain’s other Houston location at Fry Rd. and Park Row Dr. — home of zombie-apocalypse-, ski-resort-, abandoned-school-, and hospital-themed challenges — the new spot will probably house multiple rooms. It’s going in between Kura Revolving Sushi Bar’s corner restaurant off Holman St. and the recently-opened URBN Dental office a few doors south of it. [Previously on Swamplot] Map of Mid Main Lofts’ ground floor: LoopNet
The latest tenant cropping up in the Mid Main Lofts’ Main-St. side: Project Panic, a 3,395-sq.-ft. escape room venue. Judging from the size and layout of the chain’s other Houston location at Fry Rd. and Park Row Dr. — home of zombie-apocalypse-, ski-resort-, abandoned-school-, and hospital-themed challenges — the new spot will probably house multiple rooms. It’s going in between Kura Revolving Sushi Bar’s corner restaurant off Holman St. and the recently-opened URBN Dental office a few doors south of it. [Previously on Swamplot] Map of Mid Main Lofts’ ground floor: LoopNet
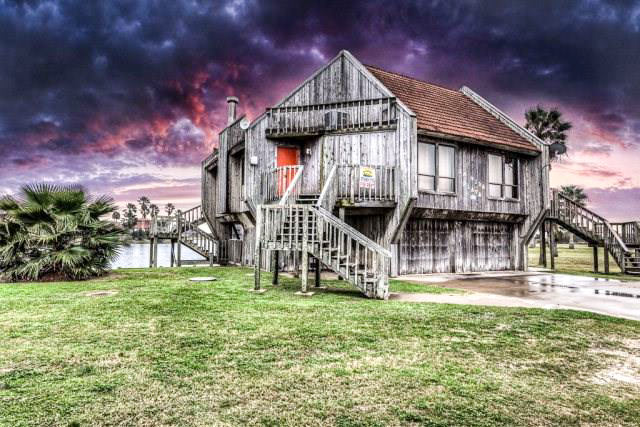


‘Tis not really the season to be renting a beach house on Matagorda Island, as the listing photos above remind us. But here’s your chance to buy one before the forecast improves. The 3-bed, 2-bath shown at top hit the market last week at $269,900.
It’s one in a set of about 2-dozen lookalikes known collectively as Bahia de Matagorda. Where does that name come from? Not Matagorda Bay proper, but rather the man-made lake at the center of the neighborhood — which lies about 6 miles south of the mainland. You’ll see the water off in the distance below:
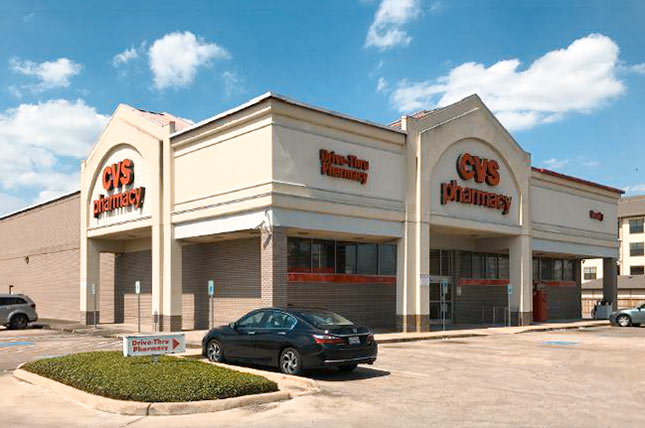


Coming soon to the former CVS Pharmacy building at Westheimer and Eldridge Pkwy.: La Michoacana Meat Market. A group with ties to the grocery chain bought the 1.9-acre property earlier this year and filed a building permit last week to get started on the conversion. The photos above show what the 19-year-old building looked like during CVS’s tenancy. It’s been sign-less for the better part of this year.
Photos: Chinh (first) Colliers (second)
WESTHEIMER WILL HENCEFORTH NOT BE CALLED UR 1093 ANYMORE, SAYS TXDOT  Before last week, TxDOT had an obscure formal name for Westheimer Rd. on the books: UR 1093. The designation — short for “urban road” — was created 23 years ago to distinguish city thoroughfares from farm to market roads, reports the Chronicle‘s Dug Begley. But “No signs were ever erected,” he writes, “and it became clear no one was going to stop calling the roads what they always had, officials said in a written briefing for transportation commissioners. The only place the urban roads ever appeared was in the internal TxDOT roadway inventory.” There, Begley counts 30 Houston-area roads that were set to set to become URs “in theory, at least.” Officials killed the designation on November 15, reinstating Westheimer’s previous pseudonym FM 1093. The only thing that really changes: where funding for those roads can come from. Had the UR designation stuck, says a TxDOT spokeswoman, they would’ve been eligible for some extra federal maintenance money aimed at cities. [Houston Chronicle ($)] Photo of Westheimer Rd. at El Real Tex-Mex Cafe west of Yoakum Blvd.: Bill Barfield via Swamplot Flickr Pool
Before last week, TxDOT had an obscure formal name for Westheimer Rd. on the books: UR 1093. The designation — short for “urban road” — was created 23 years ago to distinguish city thoroughfares from farm to market roads, reports the Chronicle‘s Dug Begley. But “No signs were ever erected,” he writes, “and it became clear no one was going to stop calling the roads what they always had, officials said in a written briefing for transportation commissioners. The only place the urban roads ever appeared was in the internal TxDOT roadway inventory.” There, Begley counts 30 Houston-area roads that were set to set to become URs “in theory, at least.” Officials killed the designation on November 15, reinstating Westheimer’s previous pseudonym FM 1093. The only thing that really changes: where funding for those roads can come from. Had the UR designation stuck, says a TxDOT spokeswoman, they would’ve been eligible for some extra federal maintenance money aimed at cities. [Houston Chronicle ($)] Photo of Westheimer Rd. at El Real Tex-Mex Cafe west of Yoakum Blvd.: Bill Barfield via Swamplot Flickr Pool
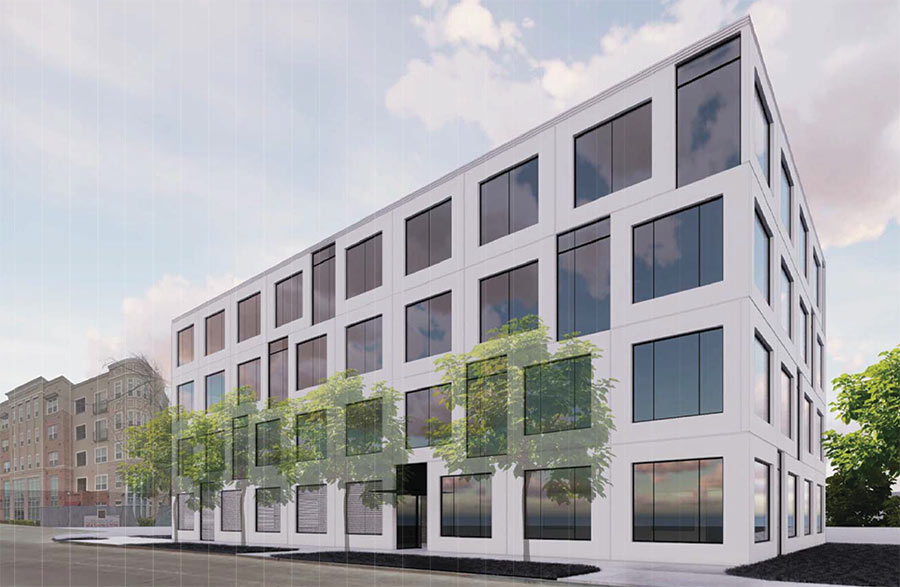

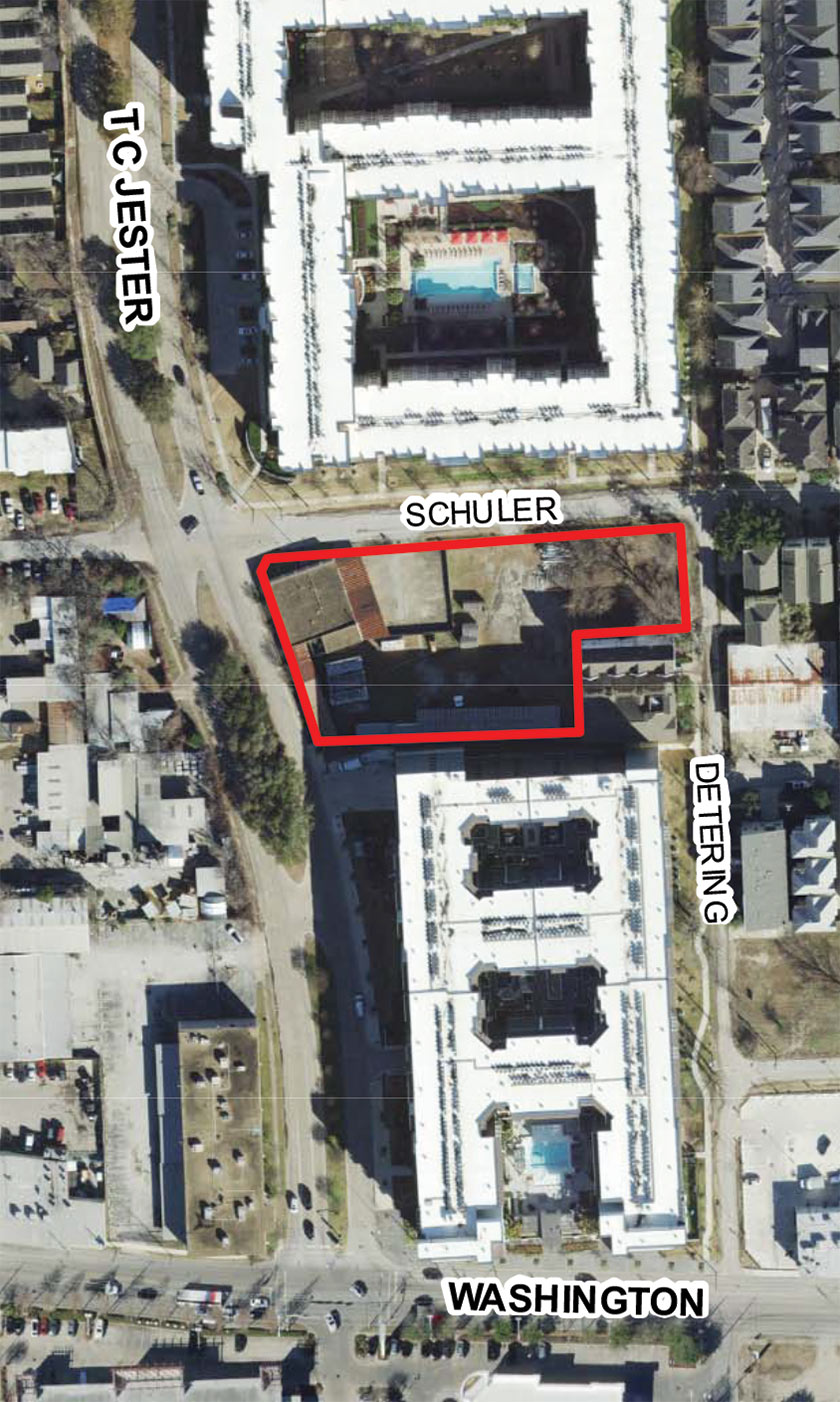
Here’s an eastward look at the new office building that could tuck in between the District at Washington and Pearl Washington apartments along T.C. Jester Blvd. north of Wash Ave. Not pictured: the parking garage and adjacent parking lot that the developer proposes to build — both to the north along Schuler St. Last week, Houston’s planning commission deferred a variance request for the site, calling the 3 curb cuts the developer had proposed along Schuler St. “excessive” and recommending it get rid of at least one before resubmitting plans.
Marshall Construction’s office and yard complex occupies the site right now and includes a southeastern carve-out for a couple of townhomes along Detering St.
PHOENIX TOWER DOUBLING DOWN ON PARKING  A new 8-story parking garage will be built next to the Phoenix Tower’s existing 8-story parking garage writes Ralph Bivins over at Realty News Report. The planned “garage annex,” he reports, “will adjoin Phoenix Tower’s original eight-story garage and also provide direct, covered access to The Hub,” the restaurant-heavy core of Greenway Plaza, between Buffalo Spdwy and Edloe St. Architect HOK has already signed up for the project, which the developer says should start before the end of the year. [Realty News Report] Photo: Parkway Properties
A new 8-story parking garage will be built next to the Phoenix Tower’s existing 8-story parking garage writes Ralph Bivins over at Realty News Report. The planned “garage annex,” he reports, “will adjoin Phoenix Tower’s original eight-story garage and also provide direct, covered access to The Hub,” the restaurant-heavy core of Greenway Plaza, between Buffalo Spdwy and Edloe St. Architect HOK has already signed up for the project, which the developer says should start before the end of the year. [Realty News Report] Photo: Parkway Properties
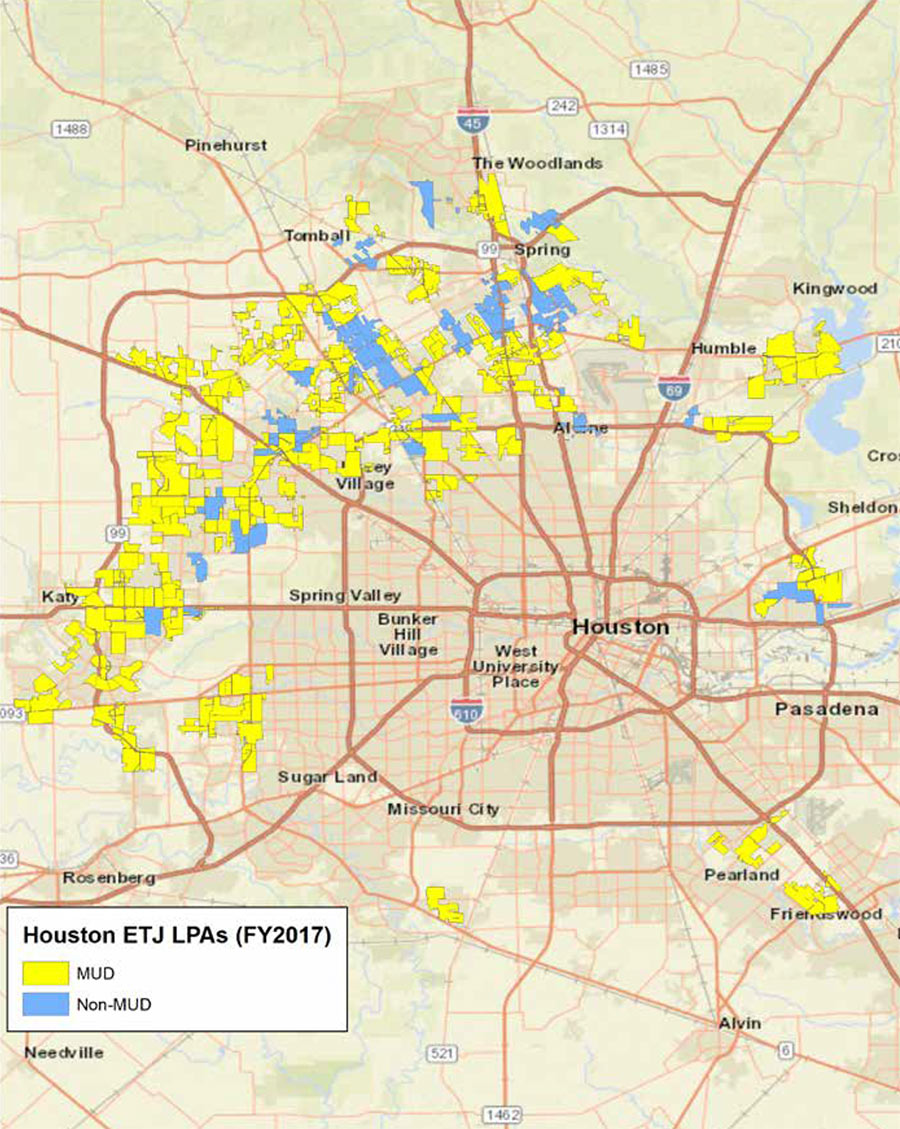
Since 1995, a new kind of land designation has been cropping up all along Houston’s outskirts: the LPA, or limited-purpose annexation. It’s a way for the city to collect sales tax in small, usually commercial, portions of unincorporated areas without formally annexing them or providing them with city services. Often LPAs are established inside an existing MUD (as shown above in yellow), although they doesn’t have to be (as shown by the blue). “The pursuit of these agreements is often framed by the city as a commuter tax,” according to a recent report from Rice’s Kinder Institute, “aimed at collecting revenue from residents who live outside of Houston but who use the services provided by the city.”
But there’s another reason why more than 200 LPAs now encircle the city, mainly between Hwy. 6 and the Grand Pkwy. Last year, the Texas legislature passed a bill that limits cities’ annexation power by allowing the communities they want to annex to hold their own referenda before their extra-territorial turf can be snatched up. One exception: A referendum isn’t necessary if the city and the area to be annexed have a preexisting agreement that says so. Many of Houston’s LPAs include this carve-out, meaning that when they expire — the typical term is 30 years — the areas they regulate will be up for grabs by the city . . . no local vote needed.

