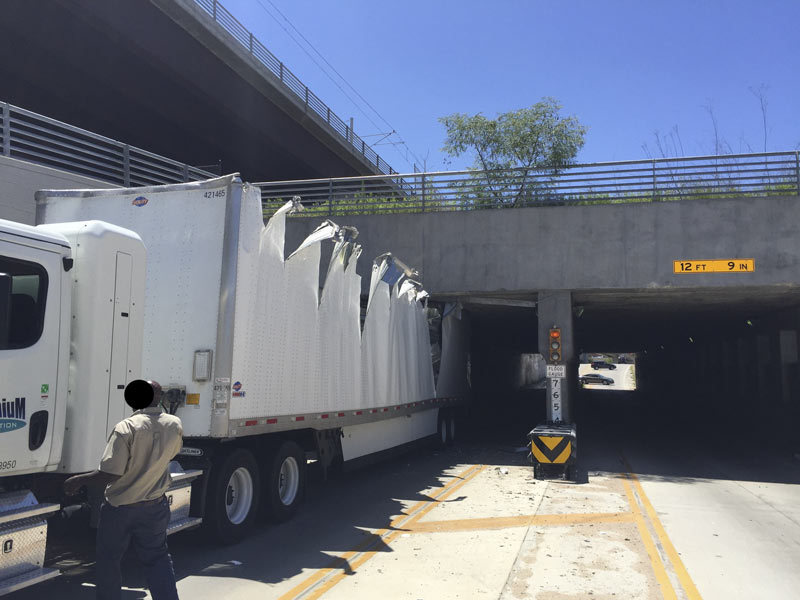

Not to be outdone by last week’s midday plug-up of the Alfred Hernandez Tunnel beneath the railroad tracks and the Burnett TC Red Line stop, another semi making its way through the passage got lodged in the tunnel late this morning — getting torn open end-to-end in the process. But that’s not even the first truck stuckage incident at the underpass in the last 24 hours, according to a reader who’s had both a camera and a Twitter account trained on the recently retooled intersection for at least the last few months.
The reader tells Swamplot that another truck got stuck briefly last night, and that it happens about 6 times a week: “Our camera system auto-wakes when it hears something beyond a certain threshold; most drive away, presumably nervous[ly] on their way to have a talk with the boss.” Some work on the tunnel has been on the city’s docket this spring, and was approved at a mid-April meeting; that’s likely to start around the end of the month.Â
Here’s the scene from above as of early this afternoon:


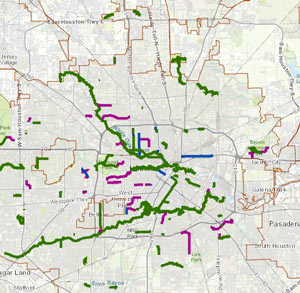 This morning’s city council meeting has the Houston Bike Plan back on the docket, following the most recent round of public-input-based tweaking to the plan (as well as a delay of the vote, which was initially scheduled for earlier this month). Over in the Chronicle Dug Begley
This morning’s city council meeting has the Houston Bike Plan back on the docket, following the most recent round of public-input-based tweaking to the plan (as well as a delay of the vote, which was initially scheduled for earlier this month). Over in the Chronicle Dug Begley 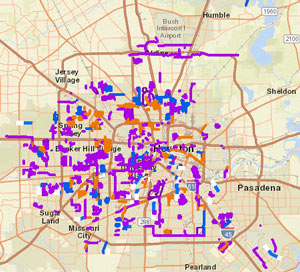 This week the state’s Fourteenth Court of Appeals upheld a
This week the state’s Fourteenth Court of Appeals upheld a  The waterway enthusiasts at Save Buffalo Bayou just issued their report on their recent tours of the waterway, with an eye toward how the scene has changed in the wake of the Tax Day flooding and the extended high flows from the try-not-to-make-things-worse paced drainage of the
The waterway enthusiasts at Save Buffalo Bayou just issued their report on their recent tours of the waterway, with an eye toward how the scene has changed in the wake of the Tax Day flooding and the extended high flows from the try-not-to-make-things-worse paced drainage of the  Taking together a recent rash of of
Taking together a recent rash of of  Another 20-year master plan for Hermann Park is currently in the works as the
Another 20-year master plan for Hermann Park is currently in the works as the  “While I am no run-off-water-channeling expert, I am under the impression that tossing out the concrete is not just for appearances. The concrete ditch moves the water faster than the natural channel, and can [thereby] actually aggravate flooding rather than cure it. Returning to the natural channel structure may mitigate flooding.” [
“While I am no run-off-water-channeling expert, I am under the impression that tossing out the concrete is not just for appearances. The concrete ditch moves the water faster than the natural channel, and can [thereby] actually aggravate flooding rather than cure it. Returning to the natural channel structure may mitigate flooding.” [ The Harris County Flood Control District is looking at removing the concrete lining from sections of the White Oak Bayou channel, writes Mihir Zaveri. The agency is conducting a study on redeveloping parts of the waterway along with the Memorial-Heights Redevelopment Authority (a.k.a. TIRZ 5); any future projects to come from the study would be within the TIRZ 5 boundaries, along sections of White Oak between roughly N. 610 and Houston St. Zaveri writes that the push “
The Harris County Flood Control District is looking at removing the concrete lining from sections of the White Oak Bayou channel, writes Mihir Zaveri. The agency is conducting a study on redeveloping parts of the waterway along with the Memorial-Heights Redevelopment Authority (a.k.a. TIRZ 5); any future projects to come from the study would be within the TIRZ 5 boundaries, along sections of White Oak between roughly N. 610 and Houston St. Zaveri writes that the push “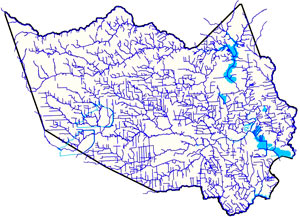 Amid the
Amid the 
 “Amazing how that works – we demolish houses and businesses next to schools to make way for parking, meaning there will be fewer homes and errand stops within walking distance of the school. Meanwhile, the Red Line is only a few blocks away, which could’ve meant fewer employees and students needing to drive there. So now we have HISD paying more money it doesn’t have on acquiring land and building parking infrastructure while simultaneously devaluing a public transit asset and decreasing the school’s user base in the area. Great recipe for success, here!” [
“Amazing how that works – we demolish houses and businesses next to schools to make way for parking, meaning there will be fewer homes and errand stops within walking distance of the school. Meanwhile, the Red Line is only a few blocks away, which could’ve meant fewer employees and students needing to drive there. So now we have HISD paying more money it doesn’t have on acquiring land and building parking infrastructure while simultaneously devaluing a public transit asset and decreasing the school’s user base in the area. Great recipe for success, here!” [ “This is less about the size and population of cities, and more about growth and how it’s handled. . . . Growth has terrible problems; rapid growth makes those problems worse, and poor planning makes them worse. But the alternative of urban decline is far worse than even rapid, poorly planned growth. It’s easy to complain about traffic and overcrowded schools, higher housing costs and overextended public services. But would you really rather live with a decaying, unused infrastructure that local government can’t afford to maintain, and schools that are shutting down and neglected? Would you rather watch as the tax base erodes and the City government goes defunct? Would you want to sell your house at a steep loss? Not me. Look at Chicago. Look at what Detroit went through. Sure, the traffic jams are a thing of the past, but at what cost? One other thing to note is that small cities and rural areas can struggle with growth, too. Look at what happened in Karnes County when the Eagle Ford Shale boom was going on. They had problems with traffic, dangerous roads, a lack of housing and skyrocketing prices, overcrowded schools . . .” [
“This is less about the size and population of cities, and more about growth and how it’s handled. . . . Growth has terrible problems; rapid growth makes those problems worse, and poor planning makes them worse. But the alternative of urban decline is far worse than even rapid, poorly planned growth. It’s easy to complain about traffic and overcrowded schools, higher housing costs and overextended public services. But would you really rather live with a decaying, unused infrastructure that local government can’t afford to maintain, and schools that are shutting down and neglected? Would you rather watch as the tax base erodes and the City government goes defunct? Would you want to sell your house at a steep loss? Not me. Look at Chicago. Look at what Detroit went through. Sure, the traffic jams are a thing of the past, but at what cost? One other thing to note is that small cities and rural areas can struggle with growth, too. Look at what happened in Karnes County when the Eagle Ford Shale boom was going on. They had problems with traffic, dangerous roads, a lack of housing and skyrocketing prices, overcrowded schools . . .” [ Money from the Gulf Coast Restoration Trust Fund, set up with part of the $18.7 billion BP paid last summer to settle with the federal government over the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, is making its way to Houston in the form of a $7.1 million grant supporting the Houston Parks Board’s Bayou Greenways 2020 project. Joe Martin of the HBJ reports that the money will be
Money from the Gulf Coast Restoration Trust Fund, set up with part of the $18.7 billion BP paid last summer to settle with the federal government over the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, is making its way to Houston in the form of a $7.1 million grant supporting the Houston Parks Board’s Bayou Greenways 2020 project. Joe Martin of the HBJ reports that the money will be